Introduction to ARIN's Database
Introduction
Perhaps ARIN’s best-known function within the Internet community is the Whois directory service. Whois is driven by a large relational database with six classes of objects, all of which interconnect to create meaningful, searchable information.
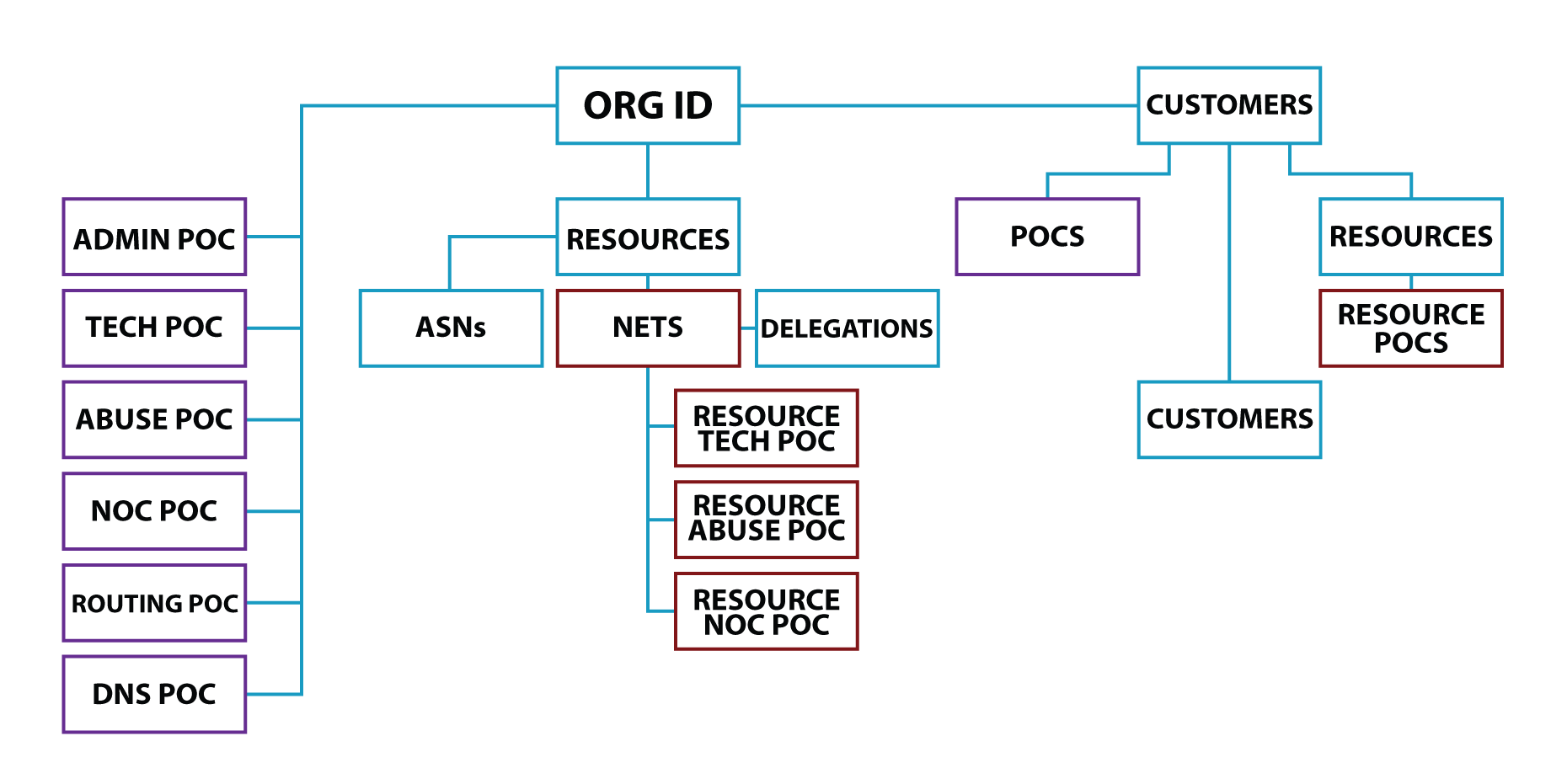
The six classes of objects are:
- Organization Identifiers (Org ID): When you think of an Org ID you can think of this as a container that holds all the other classes of objects and identifies your organization.
- Points of Contact (POC): This object identifies people or a role (group of people) within your organization that will be responsible for the day to day management of your Internet number resources.
- Autonomous System Numbers (ASNs): These represent an Autonomous System (AS) which are represented by networks that adhere to a single routing policy.
- Networks (NETs): These are IPv4 or IPv6 address blocks listed within ARIN Whois.
- Customers: These include the POCs and Resources for organizations that are associated with ARIN through a provider organization such as an Internet Service Provider. They do not have a direct relationship with ARIN, but are listed in ARIN’s Whois.
- Delegations: These are entries necessary for Reverse DNS.
Organization Identifier (Org ID) Records
An Org ID is a unique identifier representing an organization that is registered in the ARIN database. This identifier shows that entity’s name, its physical address, and any Points of Contact (POCs) that have authority over it. In addition, all Internet number resources directly assigned or allocated from ARIN, as well as any downstream resources, must be registered to the appropriate Org ID. This means you must establish an Org ID before requesting resources. An entity may maintain multiple Org IDs for different accounts, or it may consolidate all of its resources under a single Org ID. For each Org ID, there must be at least one Admin, Tech, and Abuse POC with authority over it. NOC POCs are optional.
Point of Contact (POC) Records
Point of Contact (POC) records are standalone objects that define a person, their mailing address, and their contact information, and states any organizations or resources that the point of contact has authority over. POCs can also define role accounts like noc@, abuse@, etc. An individual’s area of responsibility is defined by how their POC is connected to an organization or the resources of an organization.
Note: POCs tied to an organization are automatically inherited by any resource that organization has authority over. There is no need to create multiple POCs to accomplish this or to list the same POC on both an Organization and its resources.
Admin POC (Mandatory)
The Administrative (Admin) POC provides oversight for an Org ID and all resources it has authority over, and may be an individual or a role account. An Admin POC can only be connected directly to an Org ID, and there can be only one per Org ID. The Admin POC is permitted to update the Org ID, manage, update, request resources, and request transfers as well as manage reverse delegations.
Tech POC
The Technical POC (Tech POC) provides the day-to-day management of a resource, either through the organization to which that resource belongs, or its authority over the resource directly.
Organizational Tech POC (Mandatory)
The Organizational Tech POC is permitted to update the Org ID, manage, update, request resources, and transfer resources as well as manage reverse delegations, and may be an individual or a role account.
Resource Tech POC (Optional)
A Resource Tech POC may have authority over a resource, such as an allocation of IP address space or an Autonomous System Number (ASN), and may be an individual or a role account. This authority may be established by the Admin, Tech, or Resource Tech POC for that resource.
The Resource Tech can change the attributes of a resource, such as the resource name and the public comments displayed in Whois, and can associate Abuse, NOC, or other Tech POCs with a resource. Depending on the type of resource, the Resource Tech can specify nameservers or delegation signer (DS) records. Specifying a Resource Tech POC does not prevent the Organizational Tech POC from also making changes.
Organizational Abuse POC (Mandatory)
The Organizational Abuse POC acts as a contact for the reporting and resolution of network abuse issues, and may be an individual or role account. Multiple Abuse POCs may be specified per organization. This type of POC is not permitted to make any database changes.
Resource Abuse POC (Optional)
The Resource Abuse POC acts as a contact for the reporting and resolution of network abuse issues, and may be an individual or role account. Multiple Abuse POCs may be specified per resource. This type of POC is not permitted to make any database changes.
Organizational NOC POC (Optional)
The Network Operation Center (NOC) POC serves as a contact for network operation issues, and may be an individual or a role account. Multiple NOC POCs may be specified per organization. This type of POC is not permitted to make any database changes, and is optional.
Resource NOC POC (Optional)
The Network Operation Center (NOC) POC serves as a contact for network operation issues, and may be an individual or a role account. Multiple NOC POCs may be specified per resource. This type of POC is not permitted to make any database changes, and is optional.
Routing POC (Optional)
The Routing POC is responsible for Internet Routing Registry and Resource Private Key Infrastructure (RPKI) certification information for the organization.
Domain Name System (DNS) POC (Optional)
The DNS POC is responsible for reverse DNS and secure DNS information for the organization.
Autonomous System Number (ASN) Records
Autonomous System Numbers, or ASNs, represent Autonomous Systems: networks or connected groups of networks that adhere to a single unique routing policy that differs from the routing policies of their border peers. An ASN record, much like a NET, displays the specific Autonomous System Number and the ORG with authority over it.
Network Records
Network records define a range of IPv4 or IPv6 addresses and show the organizations and POCs with authority over them. There are three main types of resource records within the database:
- Direct Allocation : IP address space allocated directly from ARIN to an organization, either for its own use or so that it can reallocate or reassign that space to downstream customers.
- Reallocation : IP address space allocated from an organization (the upstream) to a downstream customer. The downstream customer may reallocate or reassign that space further.
- Reassignment : IP address space assigned from an organization (the upstream) to a downstream customer for its own exclusive use.
- Detailed Reassignment : Address space assigned to a customer who may need to:
- subdelegate the addresses to their own customers maintain their own in-addr.arpa delegation
- display their own point of contact (POC) information
- Simple Reassignment : Address space assigned to a customer that does NOT require the above capabilities.
- Detailed Reassignment : Address space assigned to a customer who may need to:
Customers
Customers are organizations associated with ARIN through a provider organization. Customers are searchable within Whois just as ORGs are, but may only have authority over a single network registration that is a simple reassignment.
Delegation Records
Delegations are entries that relate IP addresses to domain names using the Domain Name System (DNS) of the Internet. Delegations contain the information necessary for Reverse DNS, including the associated nameservers, and DNS Delegation Signer (DS Record) information. Unlike the other objects, delegations are not given a handle. They are searched for within Whois using a delegation name, like 0.192.in-addr.arpa.
ARIN Account Management
- Point of Contact (POC) Records & Organization Identifiers (Org IDs)
- Introduction to ARIN's Database
Related
Registration Services Help Desk
7:00 AM to 7:00 PM ET
Phone: +1.703.227.0660
Fax: +1.703.997.8844

